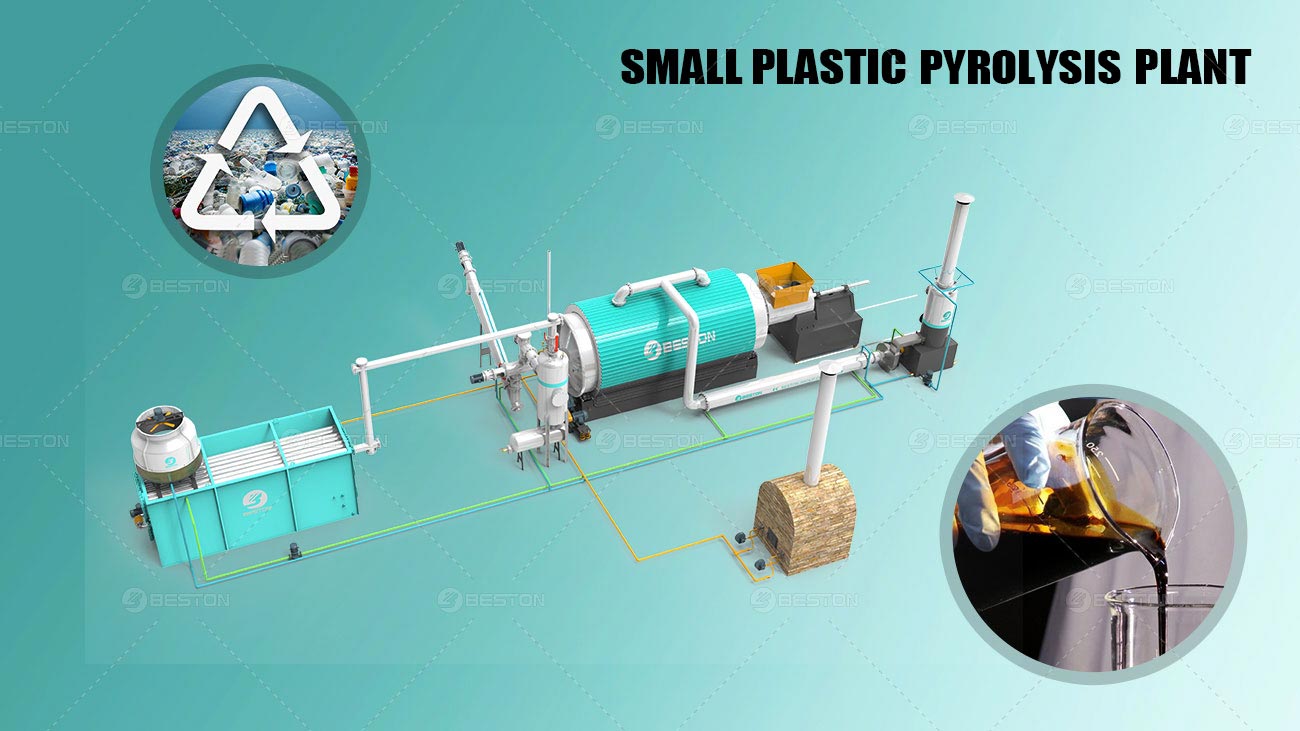
Pyrolysis plants have emerged as a crucial part of the sustainable waste management and bioresource utilization landscape. With the growing emphasis on reducing waste, generating renewable energy, and creating valuable by – products, different types of pyrolysis plants, such as continuous pyrolysis plants and small – scale pyrolysis units, are being developed and implemented worldwide. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics, applications, and the status of pyrolysis plants in the UK and Malaysia.
Continuous Pyrolysis Plants: Efficiency and Scale
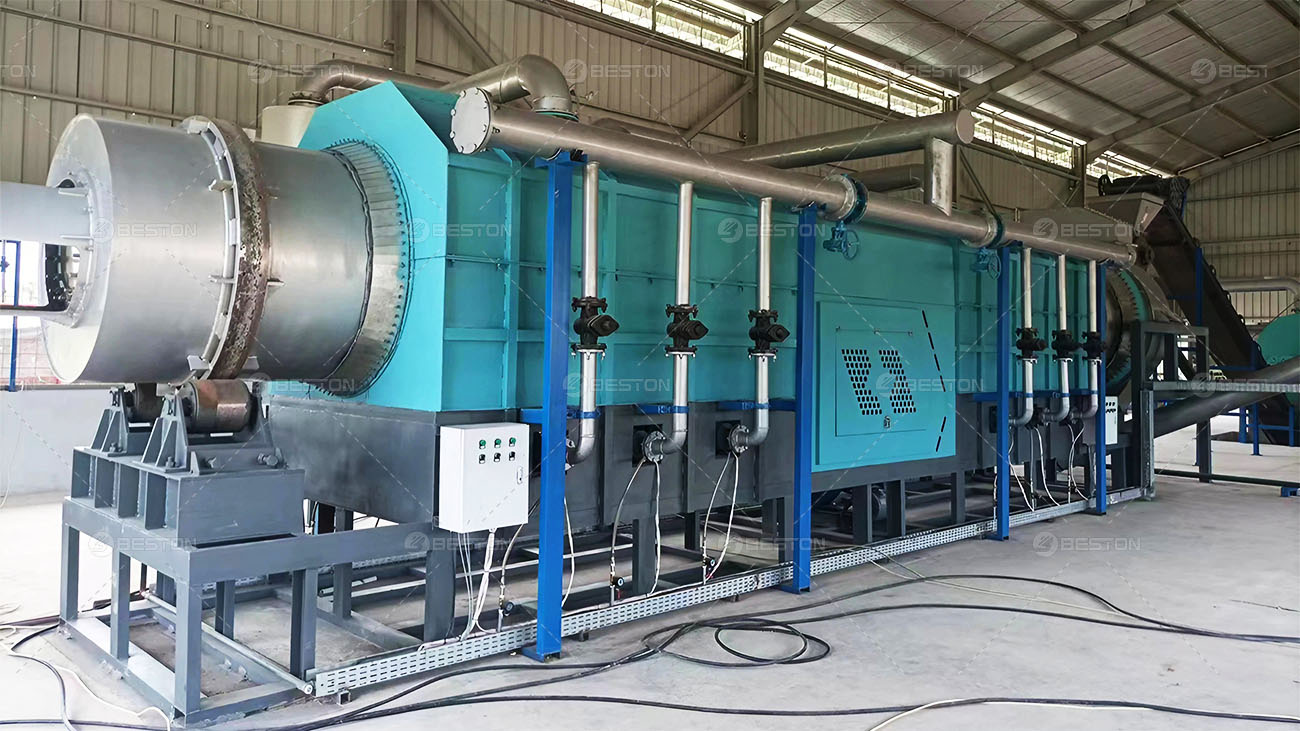
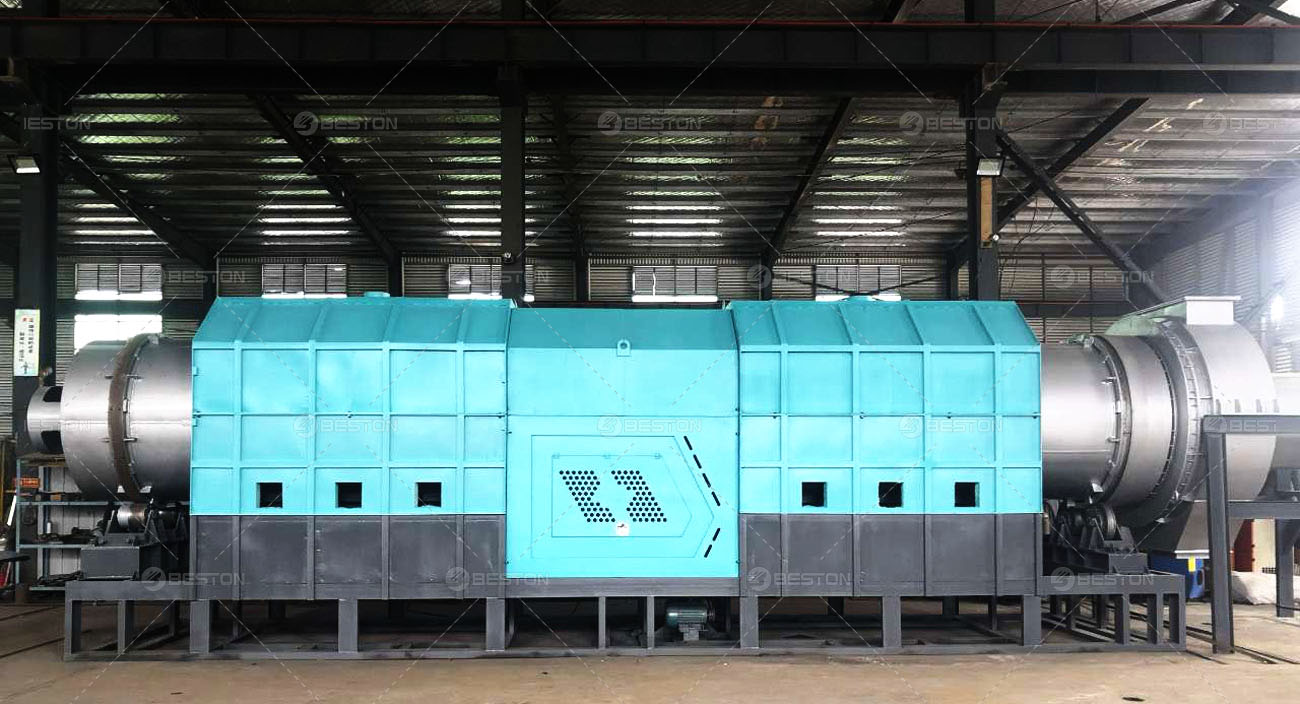
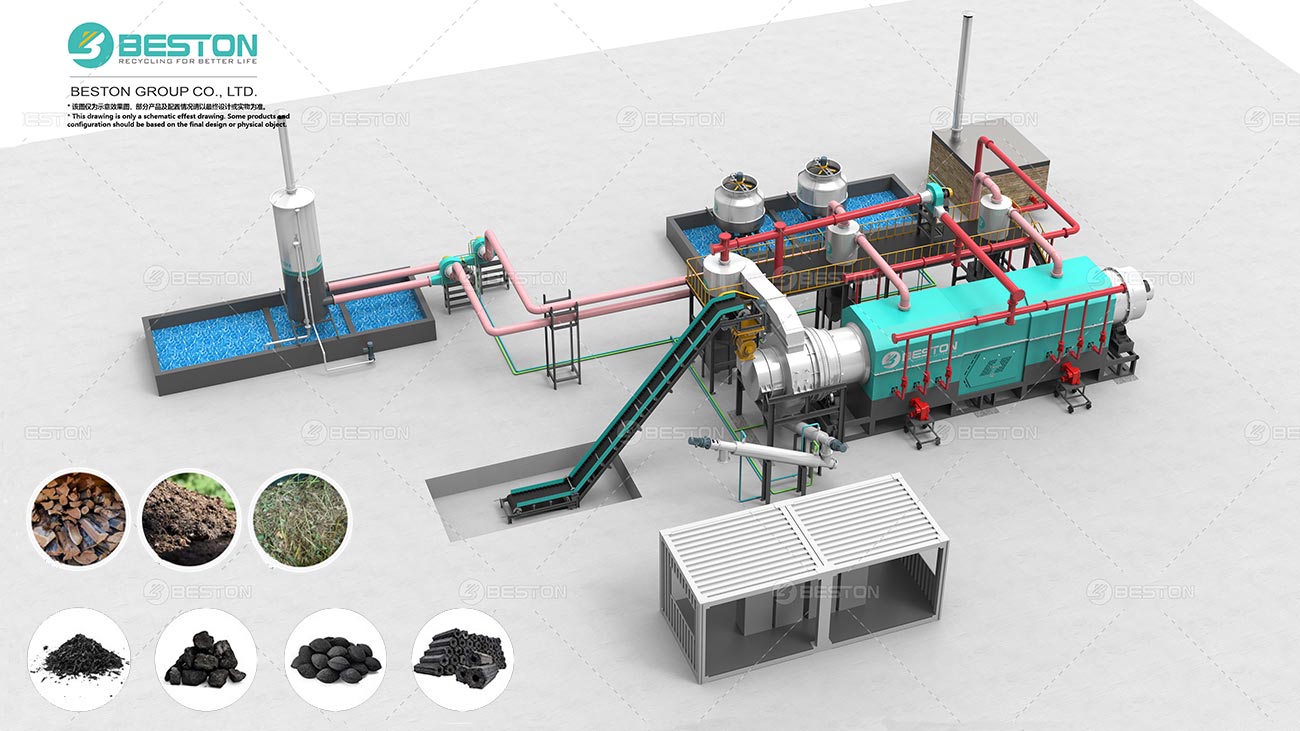
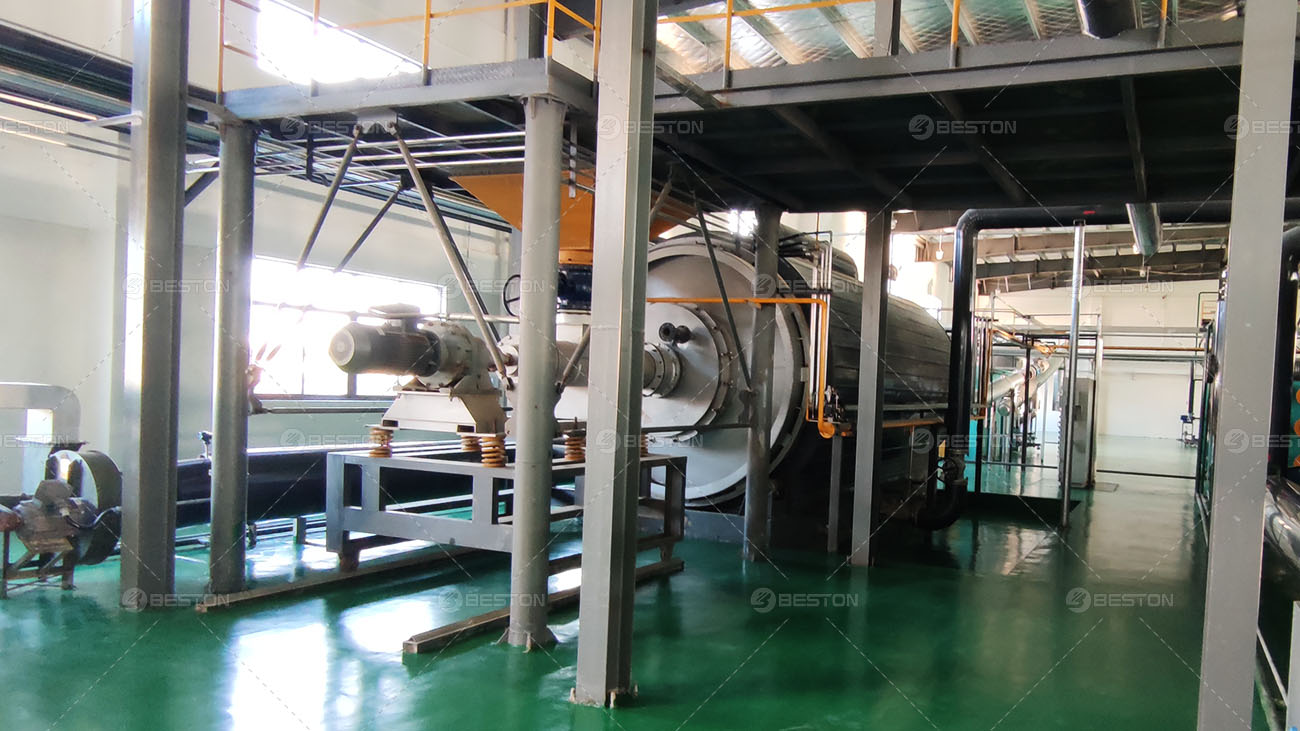
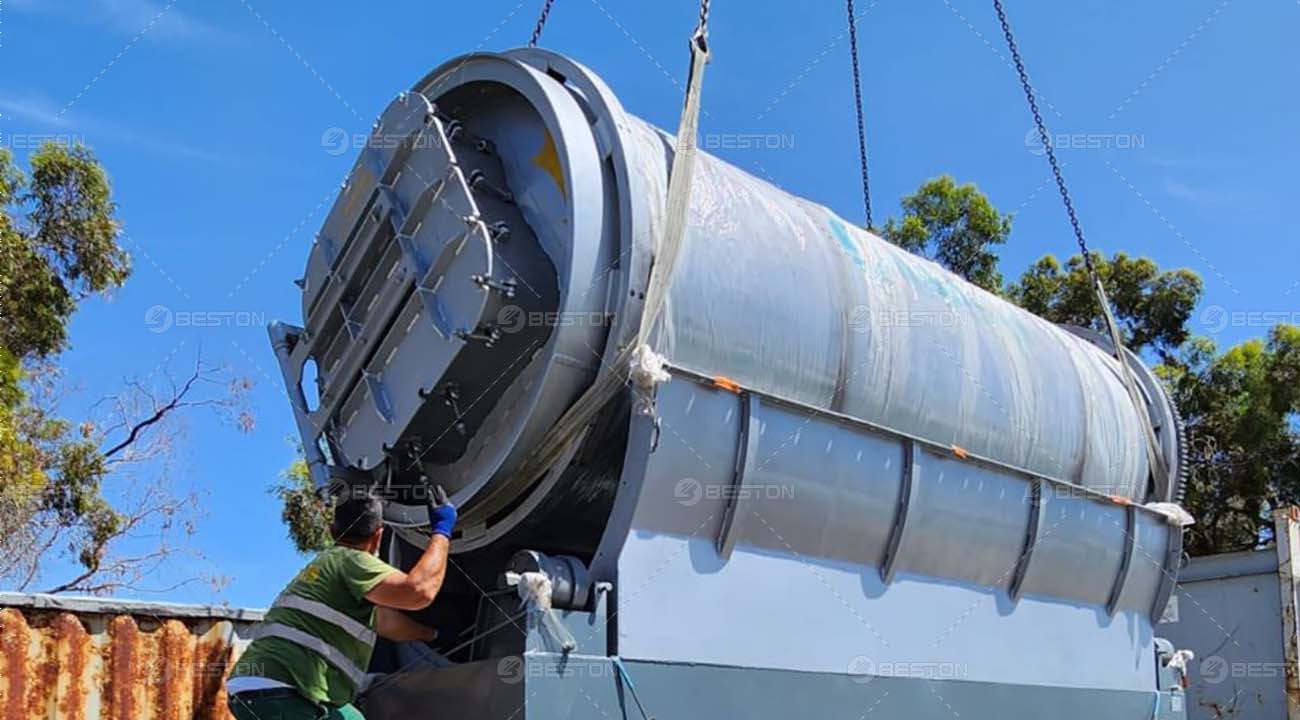
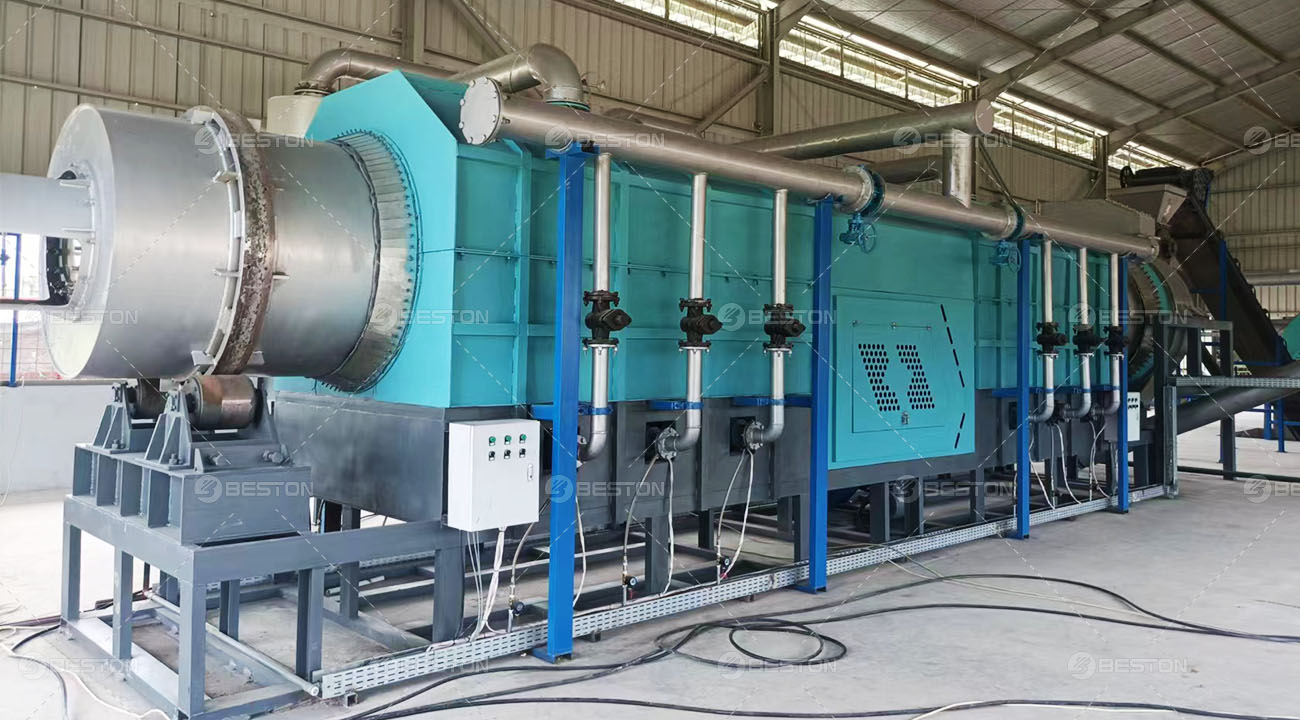
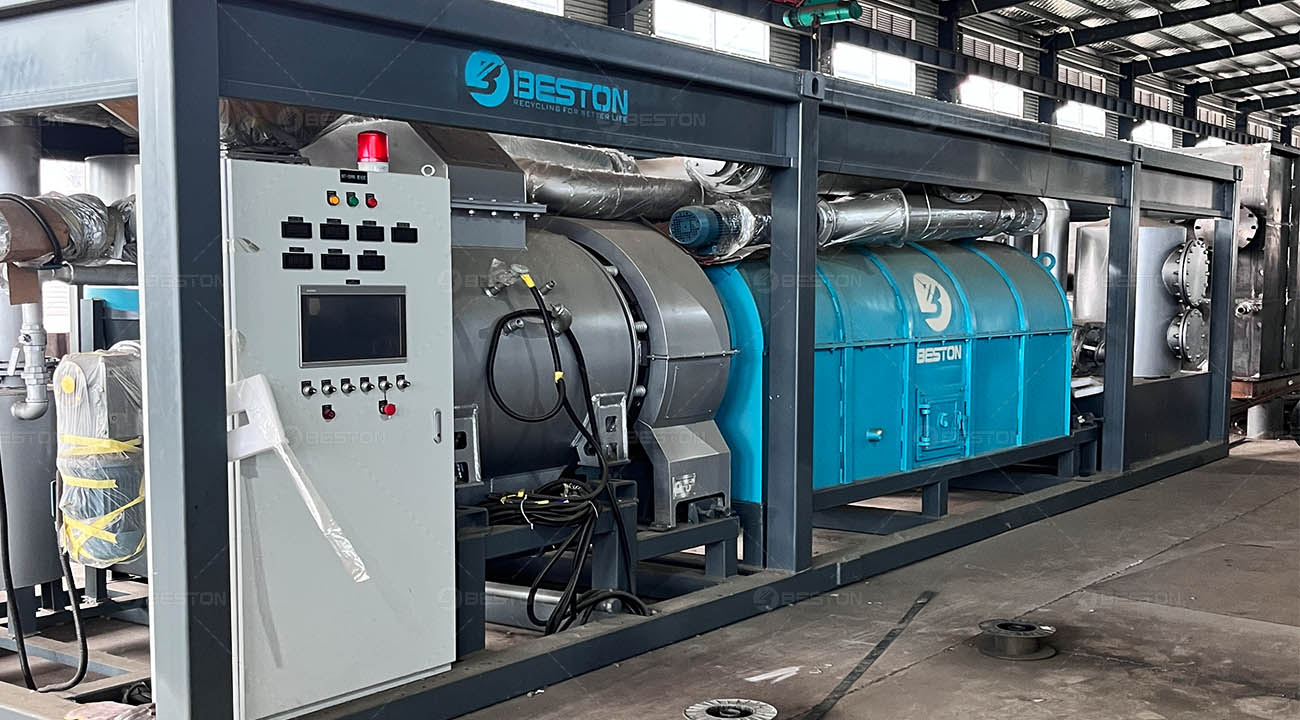
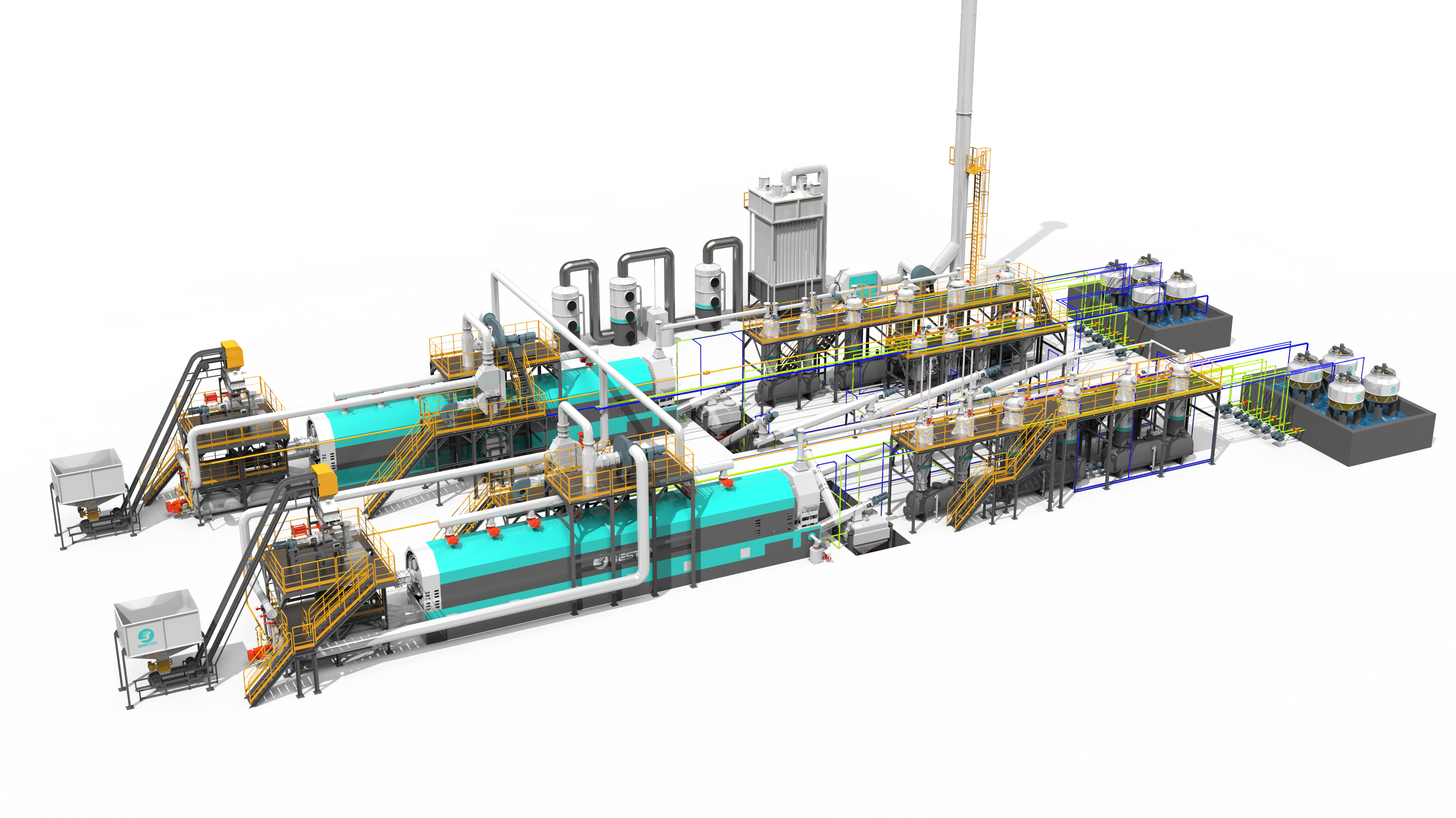
Continuous pyrolysis plants are designed to operate without interruption, allowing for a high-volume and consistent production of biochar, biofuels, and other valuable products from biomass or waste materials. These plants are equipped with advanced systems that enable the continuous feeding of raw materials, such as wood chips, agricultural residues, or even plastic waste, into the pyrolysis reactor.
The continuous nature of the process offers several advantages. Firstly, it significantly improves the overall efficiency of the pyrolysis operation. Since there are no breaks in production, the energy consumption per unit of product is reduced. The heat generated during the pyrolysis process can be better utilized in a continuous system, for example, to pre-heat the incoming raw materials or to power other parts of the plant. Secondly, continuous pyrolysis plant can produce a more uniform product. The consistent operating conditions ensure that the quality of the biochar or biofuels remains stable, which is highly desirable for commercial applications.
In large-scale waste management, continuous pyrolysis plants can handle substantial amounts of waste, diverting it from landfills and reducing the environmental impact associated with traditional waste disposal methods. They are also well-suited for industries that require a large quantity of bio-based products, such as the agricultural sector, which can benefit from the use of biochar as a soil amendment, and the energy industry, which can use biofuels produced from pyrolysis as a renewable energy source.
Small-Scale Pyrolysis Units: Flexibility and Local Applications
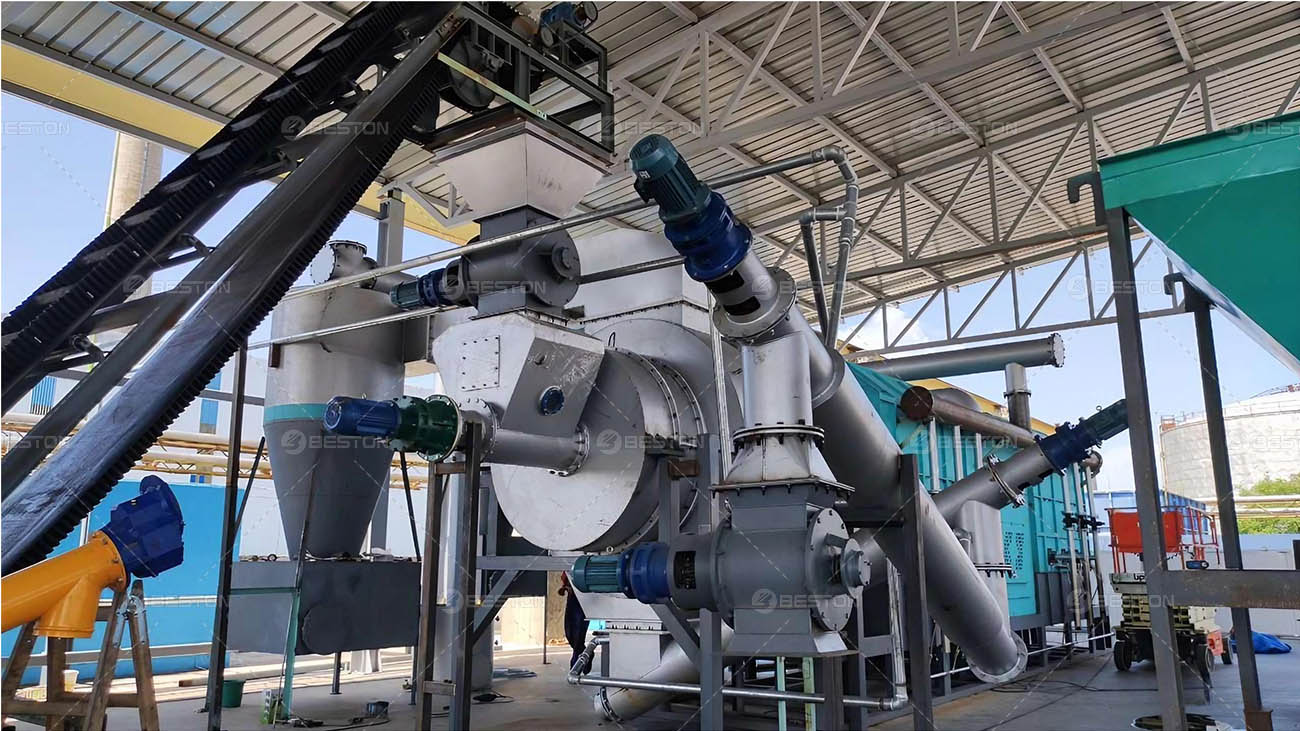
Small scale pyrolysis unit, on the other hand, offer a more flexible and decentralized approach to pyrolysis. These units are typically designed for local or on-site use, making them suitable for small-scale farmers, rural communities, or individual entrepreneurs. They are often more compact and require less capital investment compared to large-scale continuous pyrolysis plants.
Small-scale pyrolysis units can be used to process locally available biomass, such as crop residues from a small farm or wood waste from a local workshop. This not only helps in waste management at the local level but also provides an opportunity for communities to generate their own resources. For example, a small-scale pyrolysis unit can produce biochar that can be directly used on the farm to improve soil fertility, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. The biofuels produced can also be used to power local machinery or to generate electricity for off-grid areas.
Moreover, the simplicity of small-scale pyrolysis units makes them easier to operate and maintain. They can be customized to suit the specific needs and resources of the local area. Some small-scale units are even designed to be mobile, allowing for the processing of biomass at different locations. This flexibility makes small-scale pyrolysis units an attractive option for promoting sustainable development at the grassroots level.
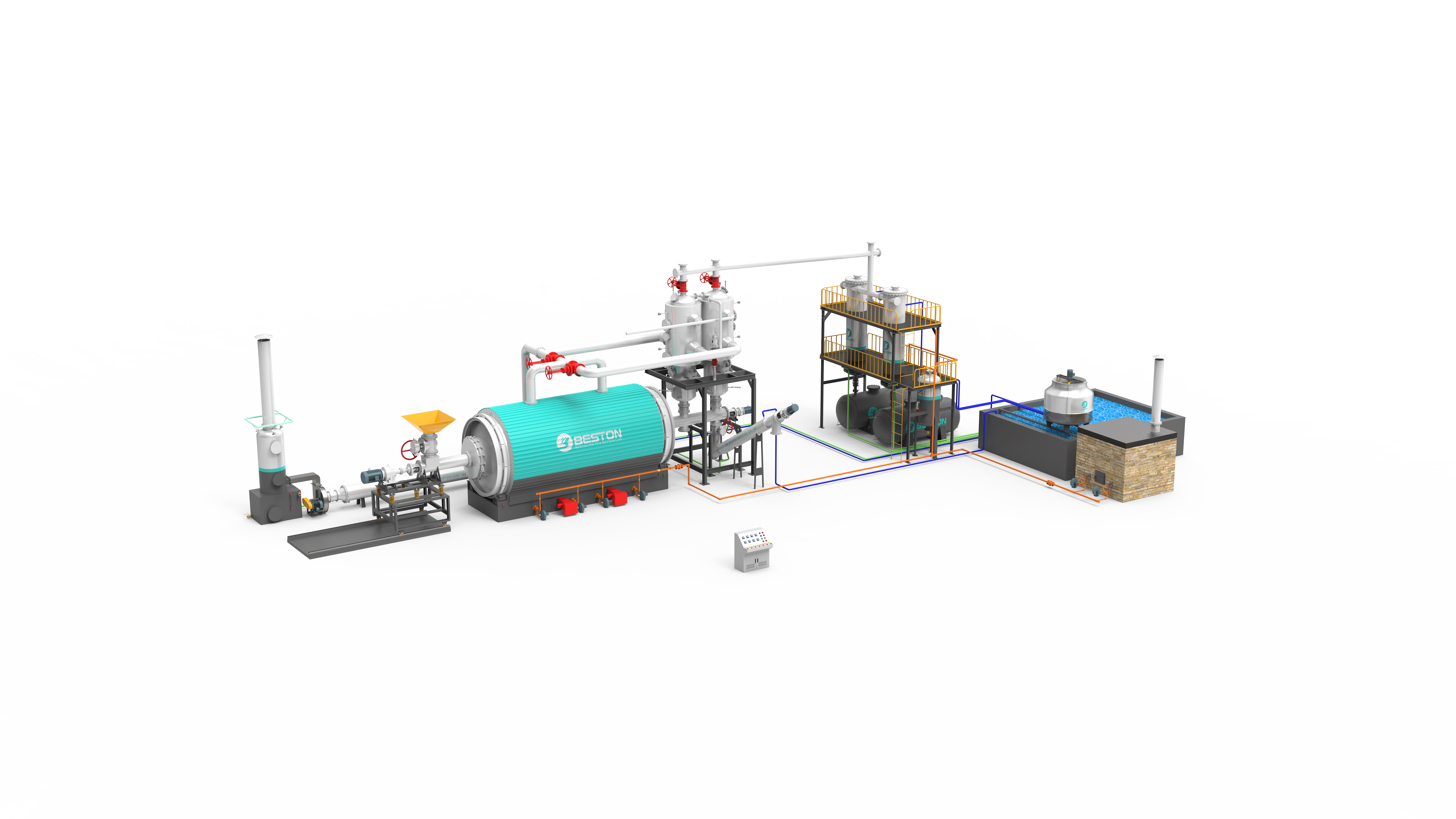
Pyrolysis Plants in the UK: A Growing Industry
In the UK, the pyrolysis industry has been steadily growing in recent years. The government’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable waste management has provided a strong impetus for the development of pyrolysis plants. There are several continuous pyrolysis plants in operation across the country, mainly focused on processing waste wood, agricultural waste, and, increasingly, plastic waste.
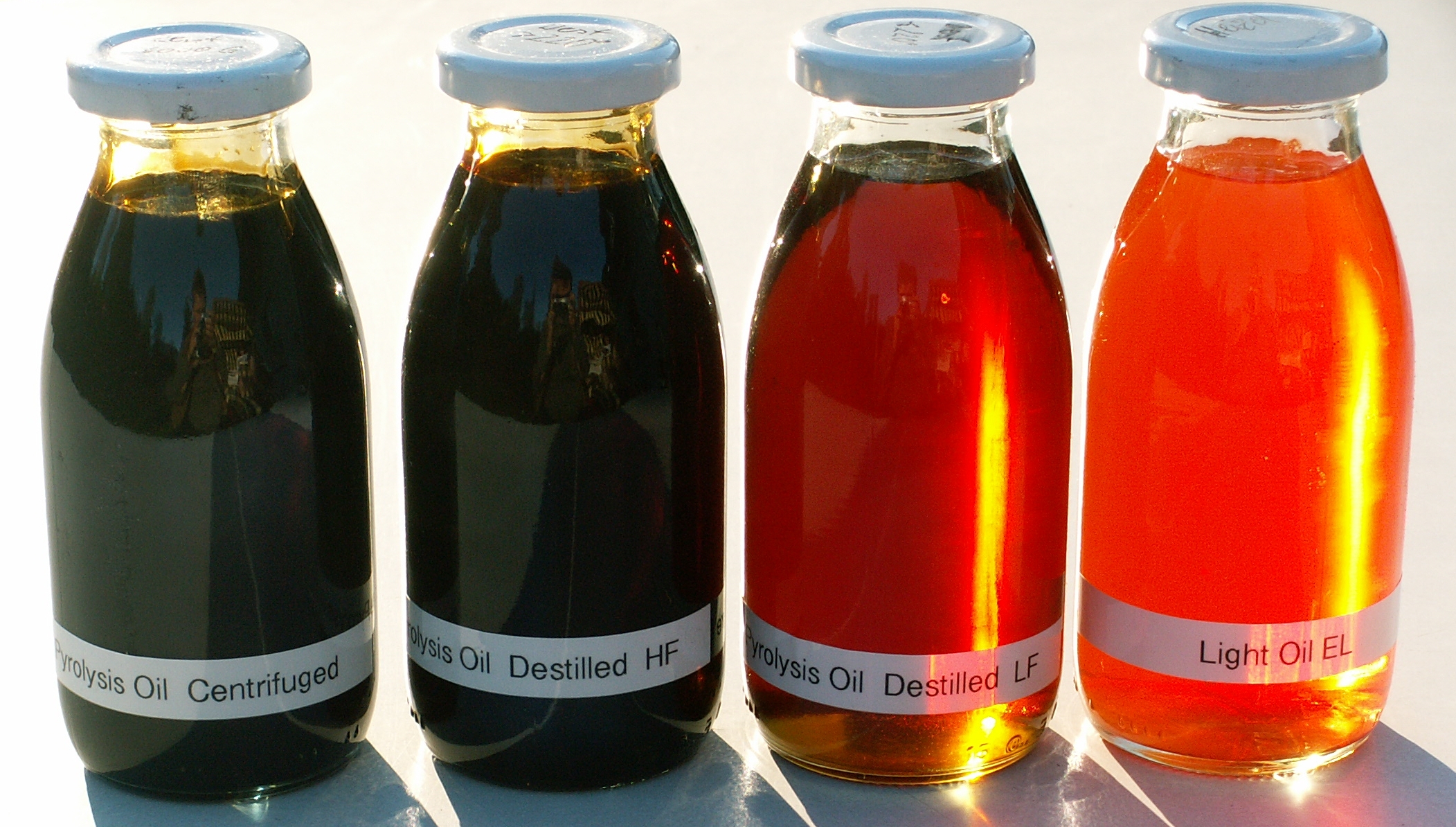
These plants play a crucial role in the UK’s circular economy initiatives. By converting waste materials into valuable products, they help to reduce the country’s reliance on virgin resources and minimize waste sent to landfills. For instance, some pyrolysis plant UK are producing high-quality biochar that is being used in large-scale agricultural projects to improve soil health and increase crop yields. The biofuels produced are also being explored for use in the transportation and heating sectors, contributing to the UK’s renewable energy targets.
In addition to large – scale plants, there is also a growing interest in small-scale pyrolysis units in the UK. Many rural communities and small businesses are adopting these units to manage their waste and generate local resources. The UK government has also provided support in the form of grants and incentives to encourage the adoption of small-scale pyrolysis technology, further fueling its growth.
Pyrolysis Plants in Malaysia: Harnessing Local Resources
Malaysia, with its abundant biomass resources, has great potential for the development of pyrolysis plants. The country has a significant amount of agricultural waste, such as palm oil empty fruit bunches and rice husks, as well as forestry residues, which can be used as feedstock for pyrolysis.
Several pyrolysis plant in Malaysia are operating, both continuous and small-scale. The continuous pyrolysis plants are often involved in large-scale projects, such as processing palm oil waste to produce biofuels and biochar. These products have a wide range of applications in Malaysia, including in the palm oil industry itself, where biochar can be used to improve soil quality in palm plantations, and in the energy sector, where biofuels can be blended with fossil fuels to reduce emissions.
Small-scale pyrolysis units are also becoming popular in Malaysia, especially among small-scale farmers and rural communities. These units provide a cost-effective way to manage agricultural waste and generate additional income. For example, some farmers are using small-scale pyrolysis units to convert rice husks into biochar, which they can then sell or use on their own farms. The Malaysian government has recognized the potential of pyrolysis technology and has been promoting its adoption through various initiatives, including research and development support and the establishment of demonstration projects.
Conclusion
Pyrolysis plants, whether continuous or small – scale, offer a sustainable and innovative solution for waste management, resource utilization, and energy generation. The continuous pyrolysis plants provide high – volume production and efficiency, while small – scale pyrolysis units bring flexibility and local – level benefits. In the UK and Malaysia, pyrolysis plants are playing an increasingly important role in promoting sustainable development, harnessing local resources, and contributing to environmental protection. As technology continues to advance and the demand for sustainable solutions grows, the future of pyrolysis plants looks promising, with potential for further expansion and innovation in both developed and developing countries.